AU Patient Summary Implementation Guide
0.5.0-preview - Preview
AU Patient Summary Implementation Guide
0.5.0-preview - Preview
This page is part of the AU Patient Summary (v0.5.0-preview: QA Preview) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. No current official version has been published yet. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
| Page standards status: Informative |
This example use case describes a possible scenario where, during a general practitioner (GP) consultation with a new patient who resides in a different state and has a usual GP, the GP retrieves an up-to-date patient summary from the patient's usual GP.
The example use cases in AU Patient Summary (AU PS) are provided for illustrative purposes only and are intended to support understanding of how patient summaries conformant to AU PS can be produced and consumed. While every effort has been made to provide useful examples, these use cases are not a normative part of the specification, nor are they fully representative of real world clinical workflows.
When reviewing clinical information such as an AU PS document, a clinician should use their clinical discretion as to the relevance of that information, as the AU PS document cannot be assumed to be complete or the most recent as it is relying on information from source systems and is not the system of record, or the system used in the creation of clinical data, rather a summary of data that can be used by a clinician as part of their clinical process to support and inform an individual's care/treatment.
Jeramy Ezra Banks, a 73-year-old man from New South Wales, has been managing chronic heart disease since his diagnosis five years ago. His regular GP, Dr Abe Lowe, oversees his ongoing care. Comfortable with basic technology, Jeramy uses a smartphone app to access and manage his health records.
Before travelling to Queensland for a holiday to visit his daughter, Jeramy confirms via the app that his patient summary has been updated by Dr Lowe following a recent hospital admission.
While on the road, Jeramy begins to feel unwell - he is gasping for breath and feels stiff after driving. He books an appointment with a local GP in Queensland, Dr Wyatt Samuels.
During the consultation, Jeramy informs Dr Samuels that his health information is available via a patient summary shared by his regular GP. Jeramy provides access using a Smart Health Link presented via his smartphone app. Dr Samuels retrieves the most recent patient summary directly from Dr Lowe’s clinical information system (CIS). The patient summary has been curated by Dr Lowe and attested at the time of update, ensuring its integrity and alignment with clinical standards.
The summary enables Dr Samuels to quickly understand Jeramy’s condition, recent treatment, and current medications - supporting safe and informed clinical decision-making during the consultation.
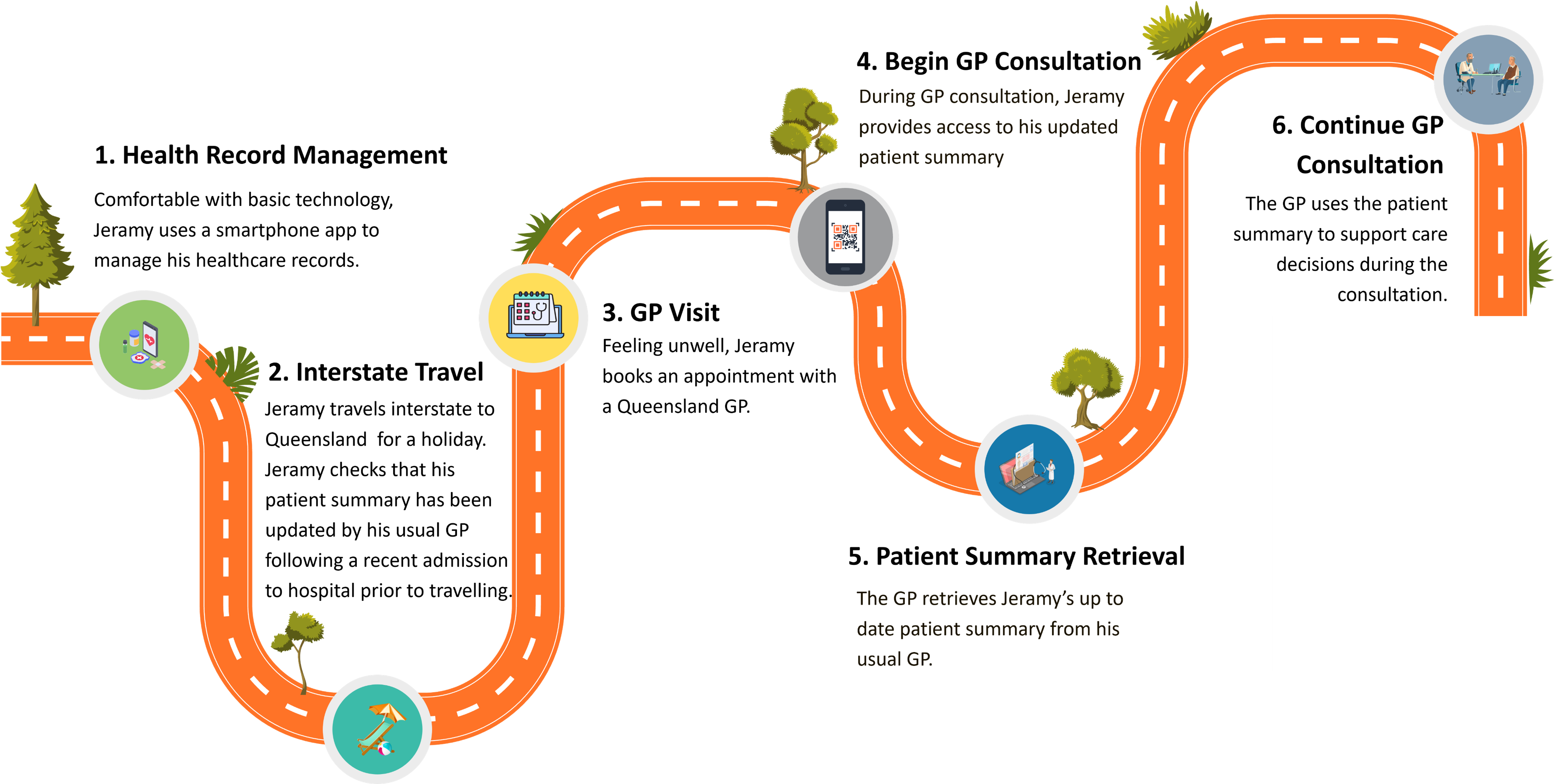
Figure 1: Interstate GP Visit consumer journey
This use case demonstrates use of patient summary during step 5. Patient Summary Retrieval of the Interstate GP Visit consumer journey.
Figure 2: Sequence diagram showing access to a patient summary via Smart Health Link
The use of Smart Health Links in this scenario reflects an emerging standard for secure sharing of patient summaries. At the time of publication, the Smart Health Link specification is still evolving, and implementers should refer to the latest guidance from HL7 International and the FHIR Infrastructure Workgroup.
The following example demonstrates both technical and clinical aspects of the use case, conforming to the AU Patient Summary requirements. Data within this example, e.g. medications, is provided by the Sparked Patient Summary Clinical Focus Group: